
Your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio is the percentage of gross income (before taxes are taken out) that goes toward your debt. Lenders will compare your income and debt in a figure known as your debt-to-income ratio. Lenders look closely at applicants who owe a large amount of debt, since it means there will be less funds to put toward a mortgage payment, even if their income is substantial. Lenders may check not only your income for the current year, but also for past years to see how steady your income has been.ĭebt:This is the total amount you owe to credit cards, car payments, child support, college loans, and other monthly debts. Your income:How much money you bring in-from work, investments, and other sources-is one of the main factors that will determine what size mortgage you can get. Here are the main things they review to determine how much you can borrow: When you apply for a mortgage to buy a home, lenders will closely review your finances, asking you to share bank statements, pay stubs, and other documents. land (where about one-third of Americans live) is located within USDA loan–eligible boundaries. While many assume USDA loans are just for farms or extremely remote areas, 97% of U.S. USDA loans:The United States Department of Agriculture offers loans in rural areas to borrowers with low to moderate incomes. In addition to putting no money down, borrowers also get lower interest rates and other fees. military (and qualifying family members) can get loans backed by the U.S. VA loans:Current and former members of the U.S.It’s ideal for first-time home buyers who lack the money for a large down payment. But if you don’t have 20%, you can put down as little as 3.5%, or in some cases 0%.įHA loan:These loans are backed by the Federal Housing Administration, which means you can put down as little as 3.5% of the price of the house.
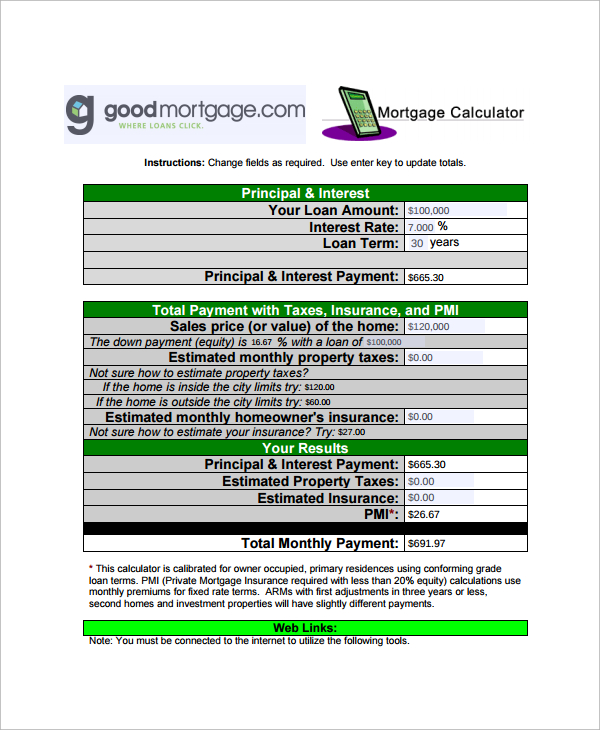
To get the best mortgage interest rates and terms, you’ll want a down payment amounting to 20% of a home’s sale price.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
